Virtual Machine Definition Computer Science
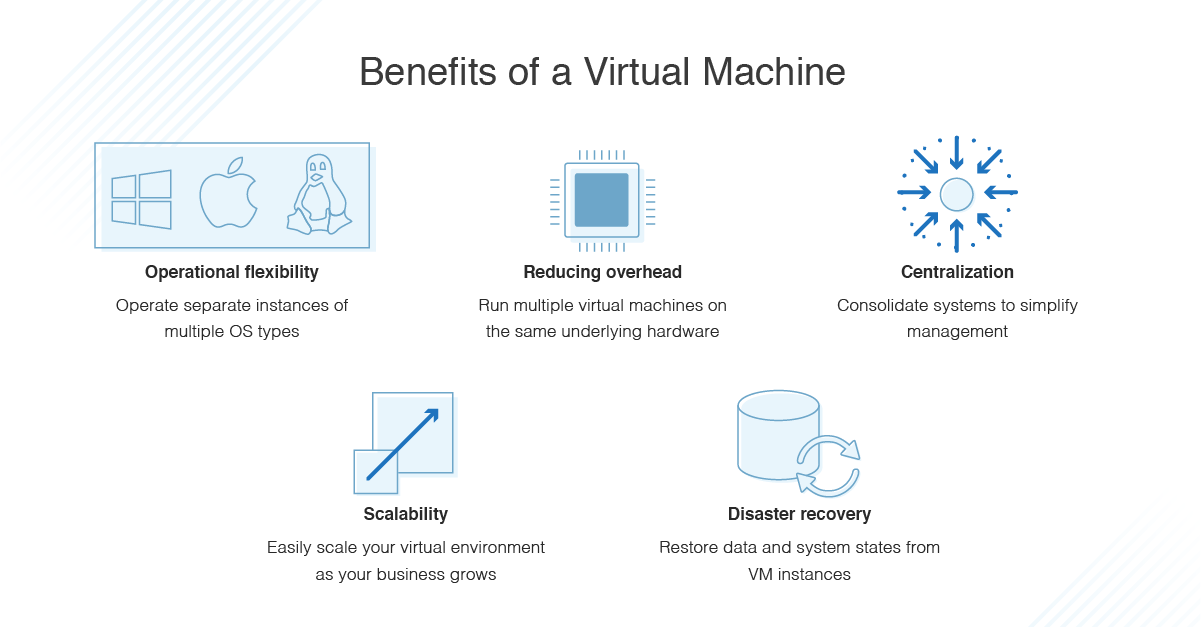
Virtual Machine Definition Computer Science. A virtual machine is a computer file, typically called an image, that behaves like an actual computer. Virtual machine software can run programs and operating systems, store data, connect to networks, and do other computing.

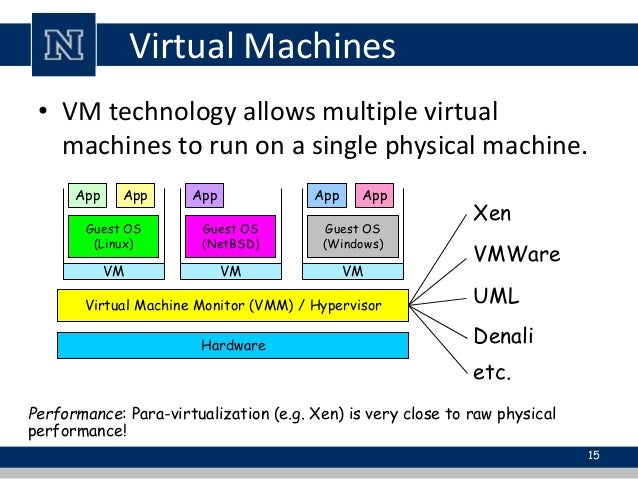
The VM shares the host's physical resources but provides a complete environment for running applications and services, similar to a physical machine without the overhead.
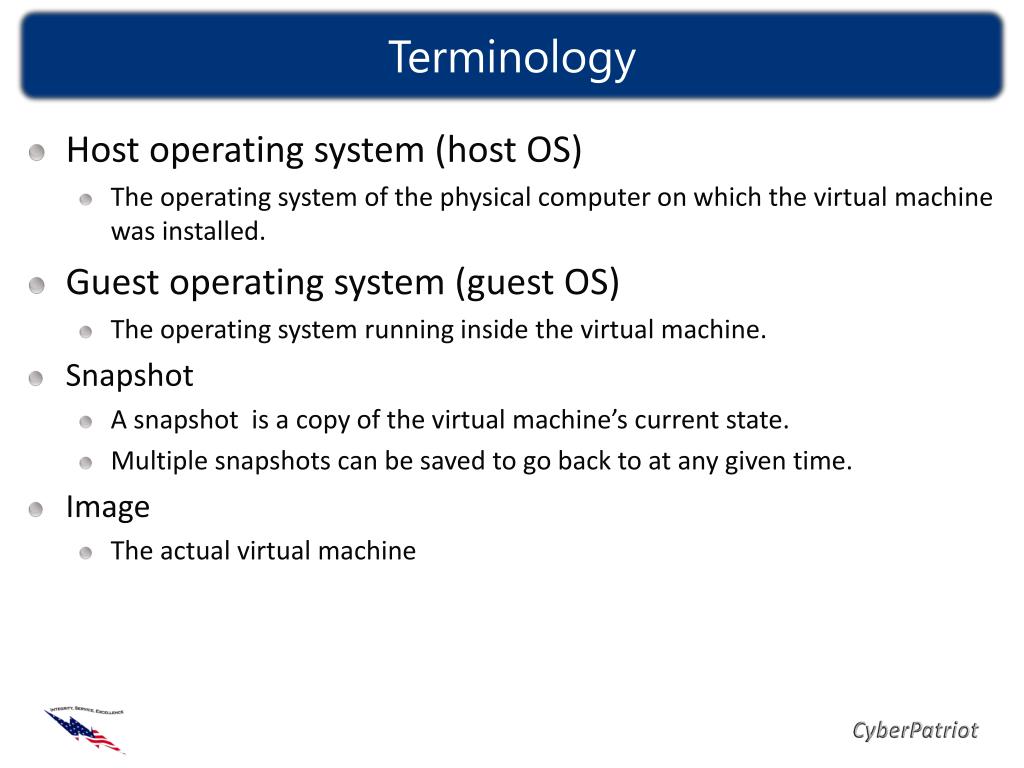
A virtual machine packages an operating system and application with a description of the compute resources needed to run it, such as the CPU, memory, storage, and networking.
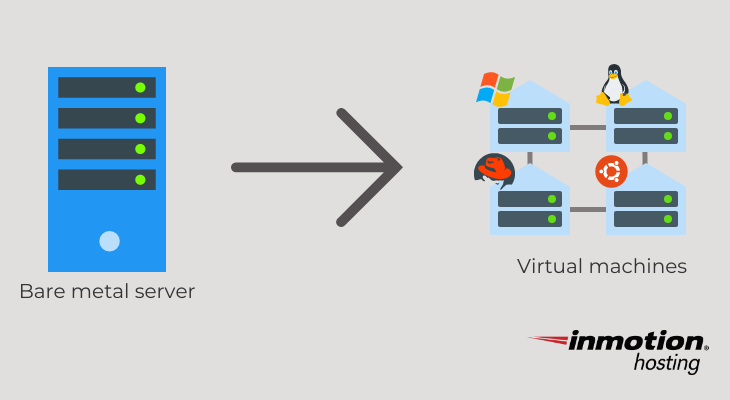
A Virtual Machine (VM) is a compute resource that uses software instead of a physical computer to run programs and deploy apps. Virtualization makes it possible to create multiple virtual machines, each with their own operating system (OS) and applications, on a single physical machine. Virtual Machine: A virtual machine (VM) is a software program or operating system that not only exhibits the behavior of a separate computer, but is also capable of performing tasks such as running applications and programs like a separate computer.